Machinery lubrication plays a critical role in industrial equipment's optimal performance and reliability.
But, contaminants such as solid particles and water can negatively impact the performance and lifespan of both lubricants and equipment. To mitigate these risks, it's essential to establish limits and standards for contamination control.
This article is intended for maintenance and reliability professionals, engineers, and equipment operators responsible for industrial machinery's performance and reliability. Establishing limits and standards for contamination control is crucial for ensuring optimal equipment performance and minimizing downtime, maintenance costs, and equipment failures. By understanding the different types of contaminants and establishing targets for each, operators can ensure that their equipment operates within acceptable limits and can take proactive measures to mitigate contamination issues before they become significant problems.
Cleanliness Standards
Determining cleanliness standards is achieved using ISO cleanliness codes. The ISO codes describe solid particles' quantity and size distribution in the lubricant. Each code is associated with a range of particle sizes and the maximum number of particles per milliliter of oil. The cleanliness code is measured using a particle counter, which uses light scattering to detect the size and quantity of particles in the lubricant.
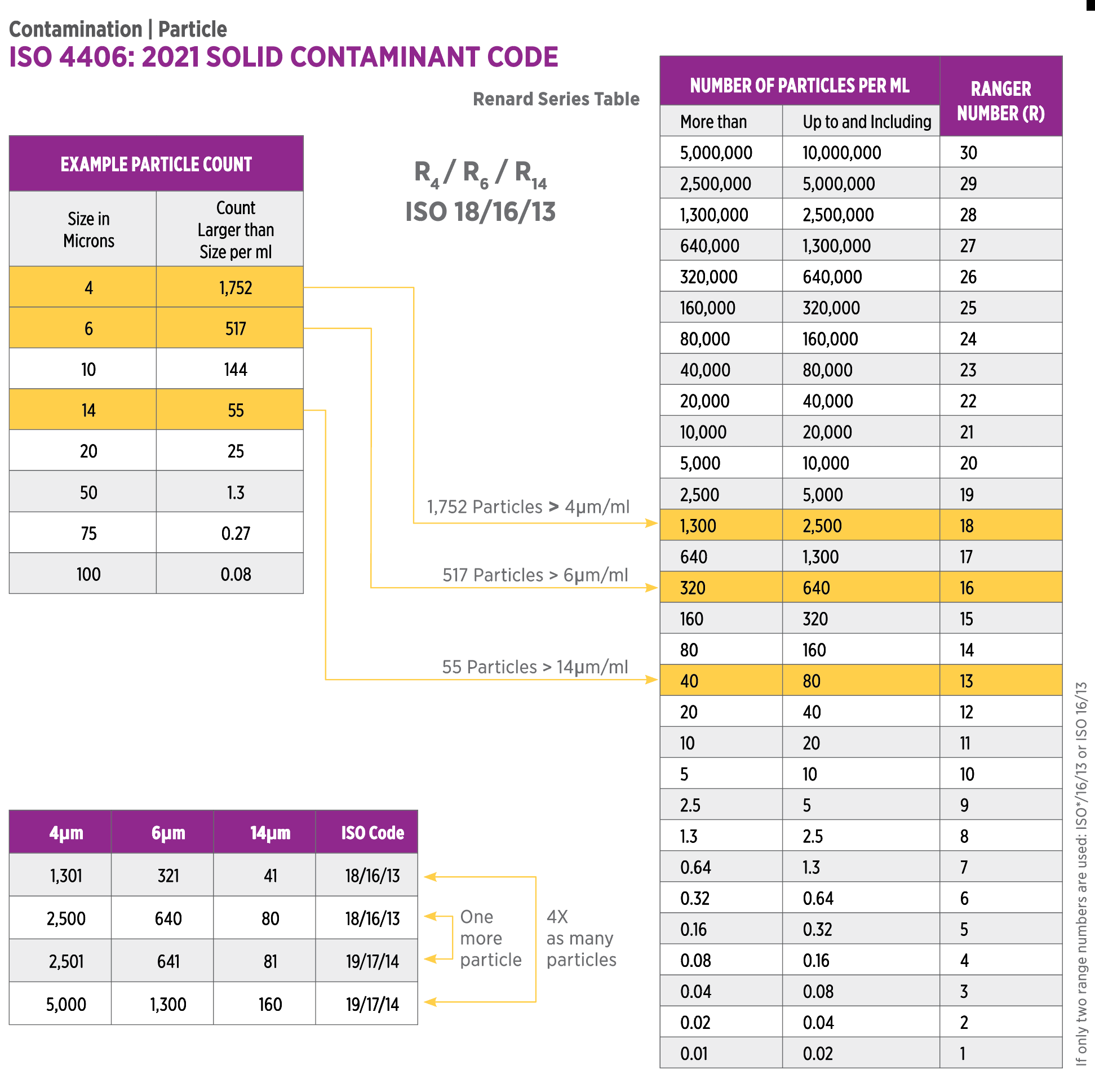 ISO 4406:2021 Contamination Chart (Source: Noria)
ISO 4406:2021 Contamination Chart (Source: Noria)
To ensure optimal performance and equipment reliability, it's crucial to establish cleanliness targets for different types of equipment. For example, equipment with tighter tolerances and high-speed components requires higher cleanliness levels than equipment with looser tolerances and slower speeds. In general, it's recommended that equipment with tight tolerances and high-speed components be maintained at an ISO cleanliness level of 16/14/11 or better. Equipment with looser tolerances and slower speeds may be maintained at an ISO cleanliness level of 18/16/13 or better.
Solid particle contamination can negatively affect lubricant and equipment performance by causing increased friction, wear, and corrosion. Strategies such as using high-efficiency filtration, keeping equipment clean and dry, and implementing proper storage and handling practices are recommended to minimize solid particle contamination.
Dryness Standards
Determining dryness standards involves establishing a maximum allowable water content in the lubricant. The maximum permissible water content varies depending on the type of equipment and lubricant used. Water contamination can negatively affect lubricant and equipment performance by causing rust, corrosion, and oxidation. Water can also reduce the lubricant's load-carrying capacity and increase the risk of cavitation.
To ensure optimal performance and equipment reliability, it's crucial to establish dryness targets for different types of equipment. Equipment with tighter tolerances and high-speed components requires lower water content levels than equipment with looser tolerances and slower speeds. In general, it's recommended that equipment with tight tolerances and high-speed components be maintained at a maximum water content level of 50 ppm or less. Equipment with looser tolerances and slower speeds may be maintained at a maximum water content level of 100 ppm or less.
Strategies such as using water-absorbing filters, keeping equipment clean and dry, and implementing proper storage and handling practices are recommended to minimize water contamination.
Contamination Targets
Lubricants can also be contaminated with other contaminants such as acids, fuel, and varnish. It's important to establish targets for each type of contaminant to ensure optimal performance and equipment reliability.
For example, the ISO has established limits for AN, which measures the acidic contaminants in the lubricant. The AN limit for most industrial gear oils is 0.5 mg KOH/g or less. The ASTM has established limits for the TAN in aviation turbine fuel. The TAN limit for turbine fuel is 0.05 mg KOH/g or less.
Things to Remember
When using new lubricants, it's important to establish limits and standards to ensure optimal performance and equipment reliability. Some key factors to keep in mind when using new lubricants include:
- Consult with the manufacturer: The lubricant manufacturer should be able to provide guidance on cleanliness and dryness standards and any other factors that may affect performance and reliability.
- Test the lubricant: Before introducing a new lubricant to the equipment, it must be tested to ensure it meets the required standards and targets. Testing can help identify any potential issues before they impact the equipment.
- Check the equipment: Once the new lubricant is used, regularly check the equipment and lubricant performance to ensure the established limits and standards are met.
- Adjust as needed: If the equipment or lubricant performance is not meeting the established limits and standards, adjustments may need to be made. This could involve changing the lubricant or adjusting maintenance and monitoring practices.
- Continuously improve: Contamination control is an ongoing process, and it's essential to constantly assess and improve strategies and practices to minimize contamination and optimize equipment performance and reliability.
Conclusion
Establishing limits and standards for contamination control is essential for ensuring optimal performance and reliability of industrial equipment. Cleanliness and dryness standards can be determined using ISO codes, and targets can be established for different contaminants such as solid particles, water, acids, fuel, and varnish. When using new lubricants, it's essential to consult with the manufacturer, test the lubricant, monitor equipment performance, adjust as needed, and continuously improve contamination control strategies. Following these guidelines, the equipment can be maintained at optimal performance and reliability levels, leading to increased productivity, reduced downtime, and cost savings.
If you're interested in implementing a comprehensive lubricant analysis program to ensure optimal equipment performance and reliability, consider the Oil Analysis Package offered by CRE Phillippines. This program includes an analysis of crucial lubricant properties such as viscosity, acidity, and contamination levels and detailed reports and recommendations for maintenance and improvement strategies. I would also help to empower your people through training in lubrication and the fundamentals of oil analysis. Contact us today to learn more about this valuable program.
Sources:
Dise, D. (n.d.). Contamination Control Objectives. MachineryLubrication. Retrieved from https://www.machinerylubrication.com/Read/31973/contamination-control-objectives
Richardson, T. (2022, October). Contamination Control Objectives: Cleanliness and Dryness. MachineryLubrication. Retrieved from https://www.machinerylubrication.com/Read/32210/contamination-control-objectives-cleanliness-and-dryness